Worldbuilding
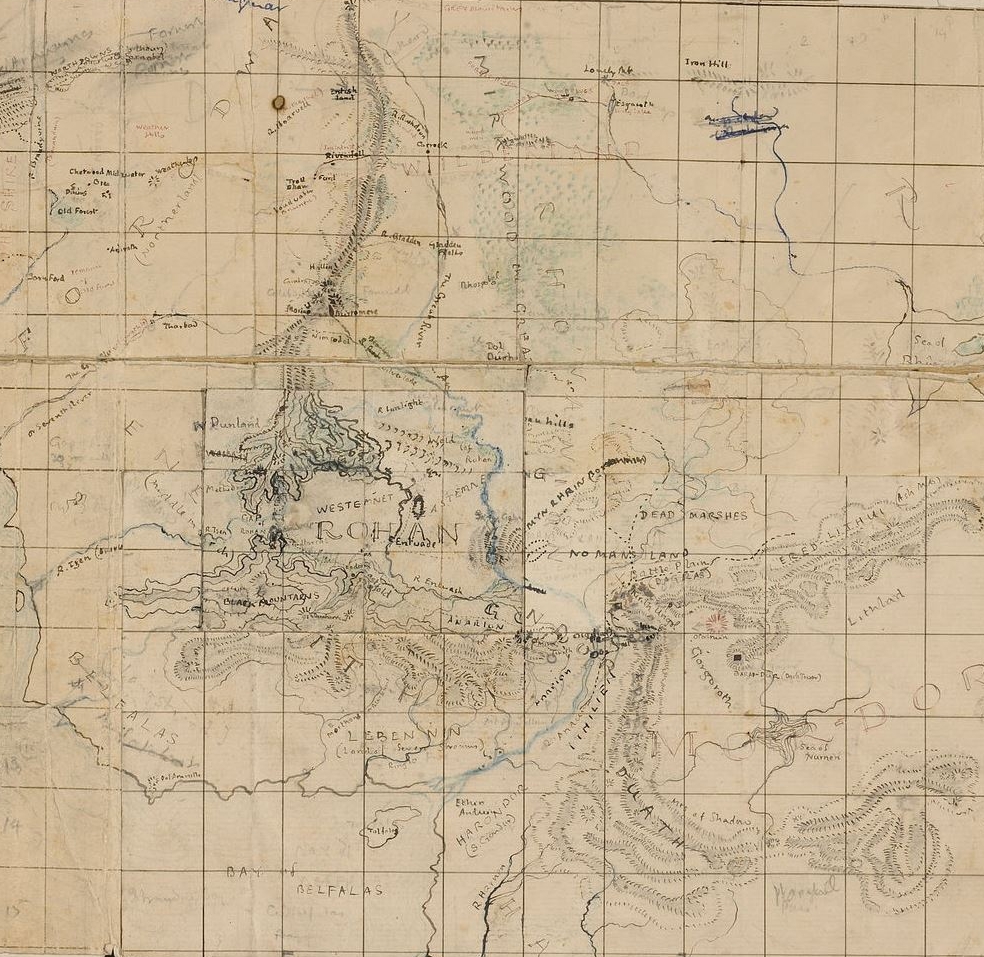
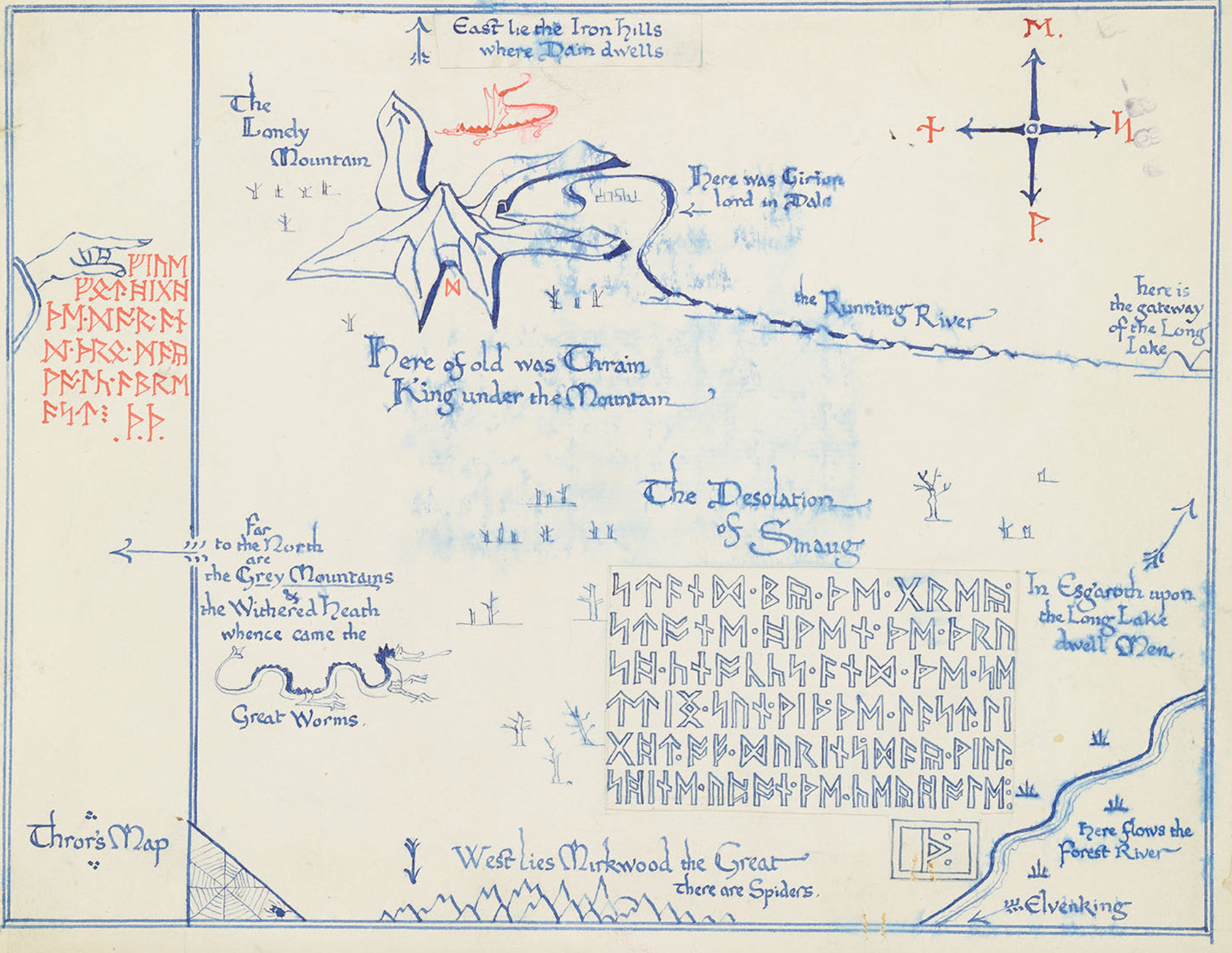
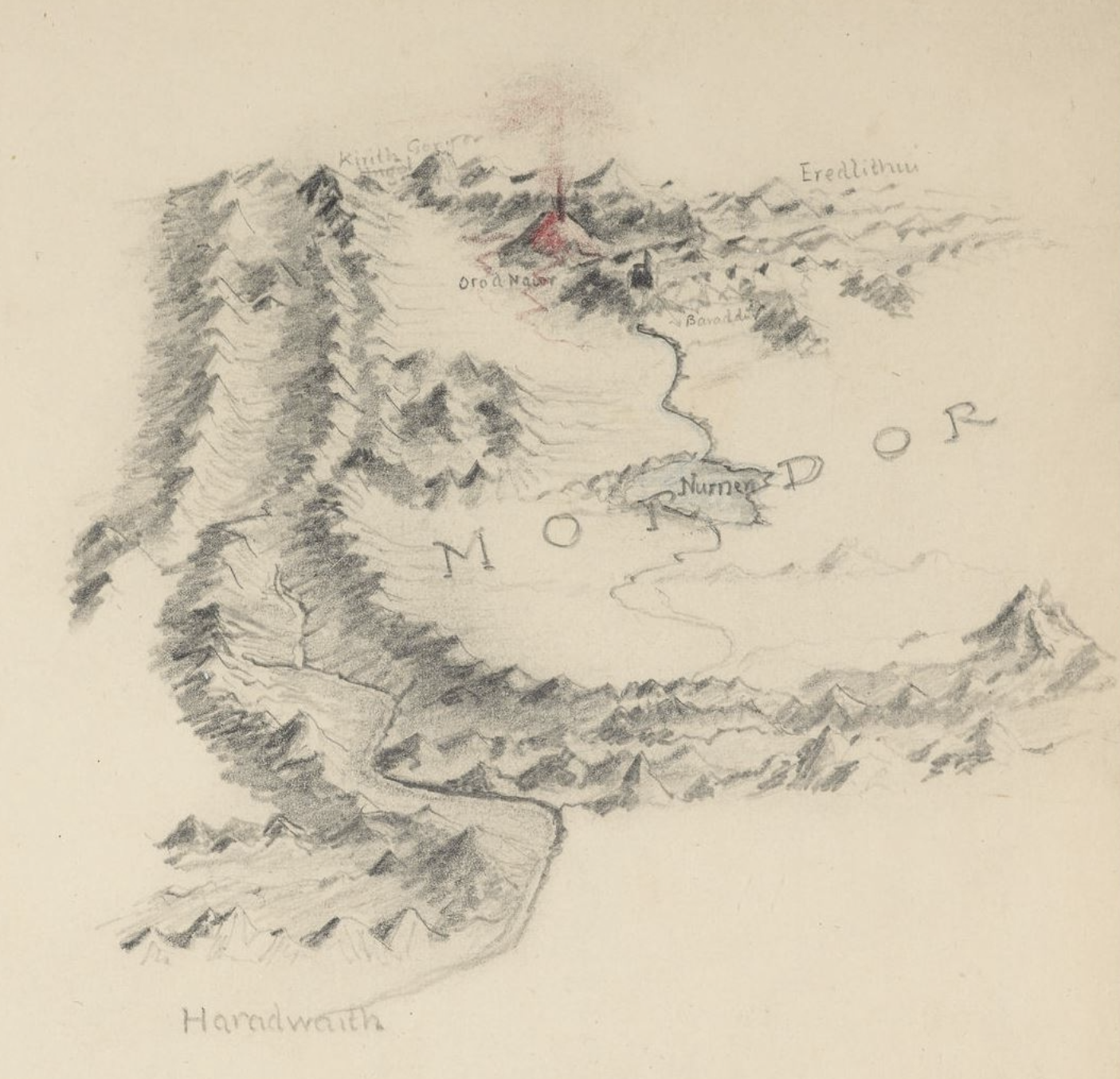
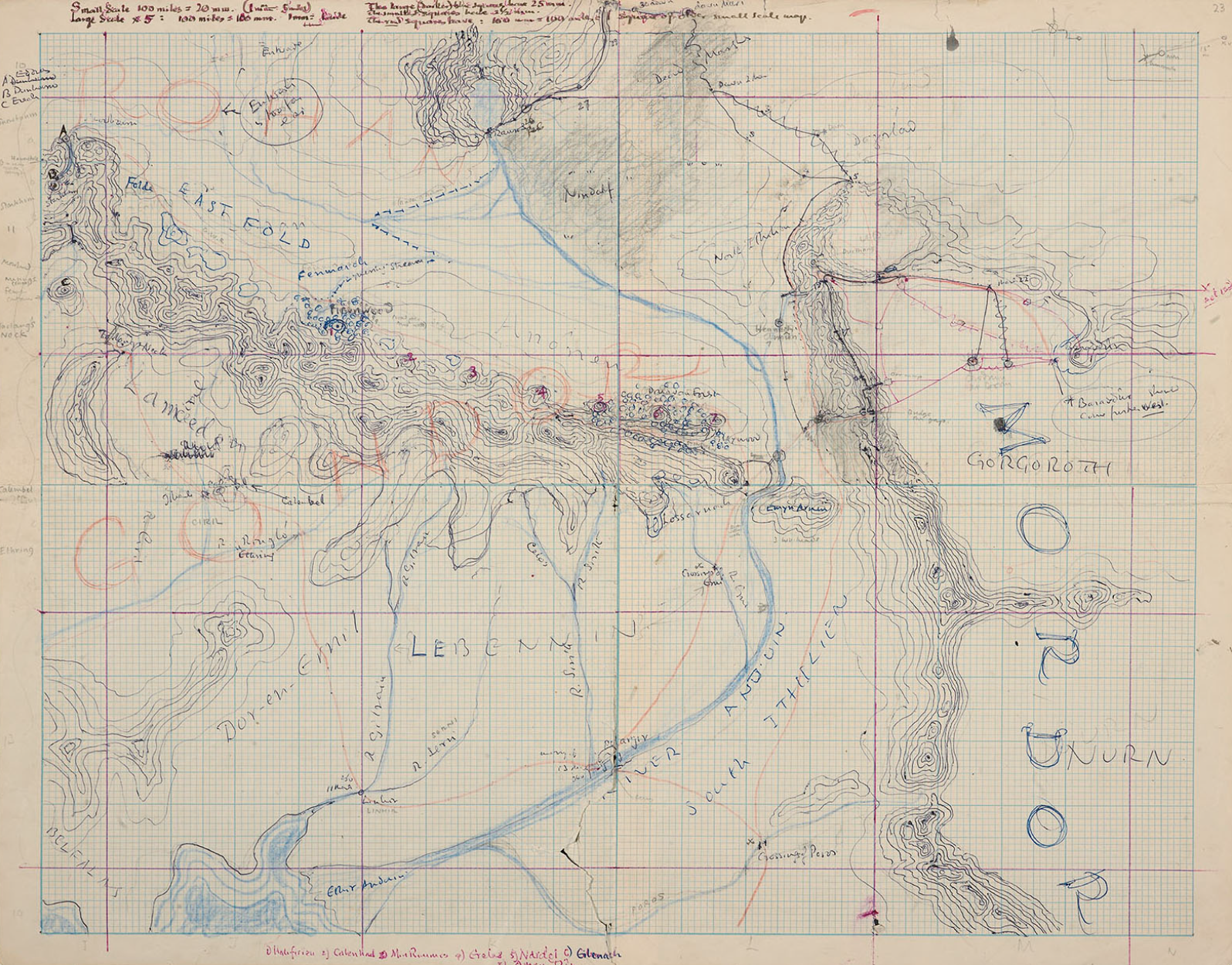
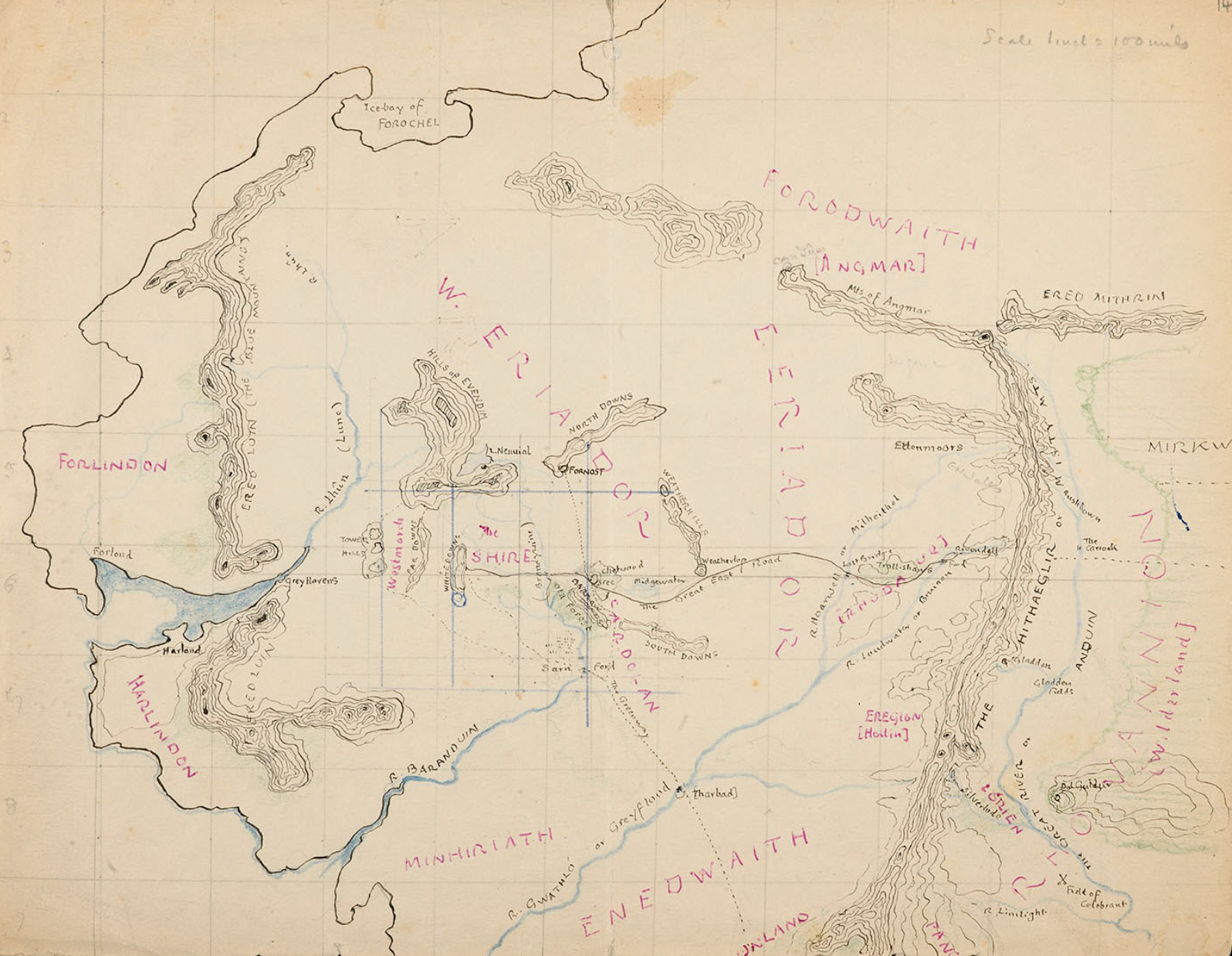
Middle-earth is the human-inhabited world, that is, the central continent of the Earth, in Tolkien's imagined mythological past. Tolkien's most widely read works, The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings, are set entirely in Middle-earth. "Middle-earth" has also become a short-hand term for Tolkien's legendarium, his large body of fantasy writings, and for the entirety of his fictional world
The setting of The Hobbit, as described on its original dust jacket, is "ancient time between the age of Faerie and the dominion of men" in an unnamed fantasy world. The world is shown on the endpaper map as "Western Lands" westward and "Wilderland" as the east. Originally this world was self-contained, but as Tolkien began work on The Lord of the Rings, he decided these stories could fit into the legendarium he had been working on privately for decades. The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings became the end of the "Third Age" of Middle Earth within Arda. Eventually those tales of the earlier periods became published as The Silmarillion and other posthumous works.